To configure networking from the ESX service console command line:
- Ensure the network adapter you want to use is currently connected with the command:
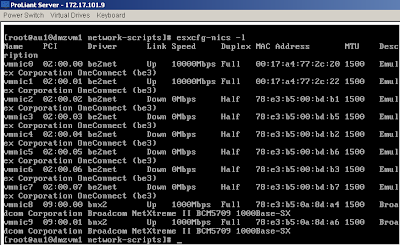
[root@server root]# esxcfg-nics –l
The output appears similar to:
Name PCI Driver Link Speed Duplex Description
vmnic0 06:00.00 tg3 Up 1000Mbps Full Broadcom Corporation NetXtreme BCM5721 Gigabit Ethernet
vmnic1 07:00.00 tg3 Up 1000Mbps Full Broadcom Corporation NetXtreme BCM5721 Gigabit Ethernet
In the Link column, Up indicates that the network adapter is available and functioning.
- List the current virtual switches with the command:
[root@server root]# esxcfg-vswitch –l
The output appears similar to:
Switch Name Num Ports Used Ports Configured Ports Uplinks
vSwitch0 32 3 32 vmnic0
PortGroup Name Internal ID VLAN ID Used Ports Uplinks
VM Network portgroup2 0 0 vmnic0
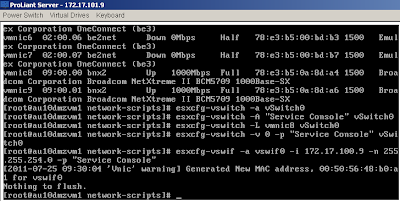
In the example output, there exists a virtual machine network named VM Network with no Service Console portgroup. For illustration, the proceeding steps show you how to create a new virtual switch and place the service console port group on it. - Create a new virtual switch with the command:
[root@server root]# esxcfg-vswitch –a vSwitch1 - Create the Service Console portgroup on this new virtual switch:
[root@server root]# esxcfg-vswitch –A “Service Console” vSwitch1
Because there is a space in the name (Service Console), you must enclose it in quotation marks.
Note: To create Service Consoles one at time, you may need to delete all previous settings. For more information, see Recreating Service Console Networking from the command line (1000266). - Up-link vmnic1 to the new virtual switch with the command:
[root@server root]# esxcfg-vswitch –L vmnic1 vSwitch1 - If you need to assign a VLAN, use the command:
[root@server root]# esxcfg-vswitch -v-p “Service Console” vSwitch0
whereis the VLAN number. A zero here specifies no VLAN. - Verify the new virtual switch configuration with the command:
[root@server root]# esxcfg-vswitch –l
The output appears similar to:
Switch Name Num Ports Used Ports Configured Ports Uplinks
vSwitch0 32 3 32 vmnic0
PortGroup Name Internal ID VLAN ID Used Ports Uplinks
Service Console portgroup5 0 1 vmnic0
Switch Name Num Ports Used Ports Configured Ports Uplinks
vSwitch1 64 1 64 vmnic1
PortGroup Name Internal ID VLAN ID Used Ports Uplinks
Service Console portgroup14 0 1 vmnic1 - Create the vswif (Service Console) interface. For example, run the command:
[root@server root]# esxcfg-vswif –a vswif0 –i 192.168.1.10 –n 255.255.255.0 –p “Service Console”
[‘Vnic’ warning] Generated New Mac address, 00:50:xx:xx:xx:xx for vswif0
Nothing to flush. - Verify the configuration with the command:
[root@esx]# esxcfg-vswif –l
Name Port Group IP Address Netmask Broadcast Enabled DHCP
v swif0 Service Console 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.255 true false - Verify the networking configuration on the ESX host. See Verifying ESX host networking configuration on the service console (1003796) .URL: